Dai Xiaohu: Current Status and Development Trend of Sludge Treatment and Disposal in China
In recent years, sludge treatment and disposal technology in China has made certain progress, and the policies and standards for sludge treatment and disposal are gradually improving. However, in the face of social development’s higher requirements for biomass energy and environmental quality, sludge treatment and disposal in China should aim at harmlessness and use resources as a means to achieve safe sludge treatment, disposal and recycling to solve the problem. The ultimate way out of sludge.
As China’s economy continues to develop rapidly and steadily, the scale of urban sewage treatment in China is increasing, and the output of sludge is also increasing accordingly. According to statistics, China’s sludge output has exceeded 60 million tons in 2019 (calculated with a moisture content of 80%), and it is estimated that China’s annual sludge output will exceed 90 million tons in 2025. However, due to long-term “heavy water over sludge”, sludge treatment and disposal have not been upgraded simultaneously with sewage treatment, the problem of sludge treatment and disposal has not been effectively solved, and the situation is very serious.
Quality characteristics of sludge in China and status quo of treatment and disposal
The nature of the sludge
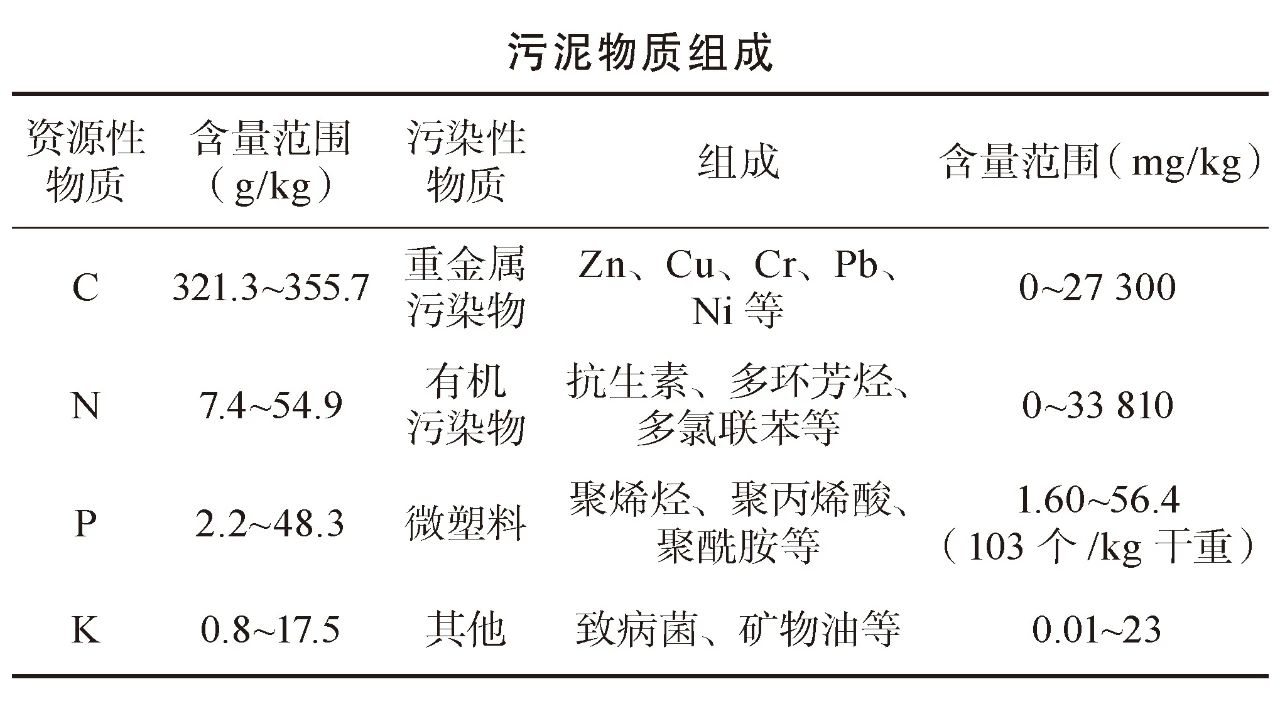
As a by-product of sewage treatment, sludge is enriched in sewage pollutants (heavy metals, refractory organics, persistent organics, microplastics, etc.) and nutrients (C, N, P, etc.), and has the dual attributes of "resources" and "pollution" at the source.The rich organic matter contained in the sludge can be processed through anaerobic treatment to obtain fuels with high calorific value such as methane biogas (biogas) and hydrogen (H2). In addition, the abundant resources in the sludge can be recovered through techniques such as protein extraction. The treated stable products can also realize land use (nutrients, organic matter stabilization treatment products) and building materials use (inorganic matter), etc., so as to realize the stabilization, harmlessness and resource utilization of sludge.
Compared with developed countries, urban sewage treatment plant sludge in China has the characteristics of low organic matter content, high sand content, and large output. Therefore, the selection of sludge treatment and disposal technology routes should be combined with the specific properties of urban sewage treatment plant sludge in China, and fully consider the dual attributes of "resources" and "pollution" of sludge to maximize environmental, economic and social benefits.
Current status of sludge treatment and disposal in China
The national “Water Ten Articles” clearly stated that the sludge produced by sewage treatment facilities should be stabilized, harmless and recycled, and the treatment and disposal of substandard sludge should be prohibited from entering the cultivated land, so as to ensure the safe disposal of the sewage plant sludge, and the treatment process and disposal links will not cause secondary pollution to the environment.
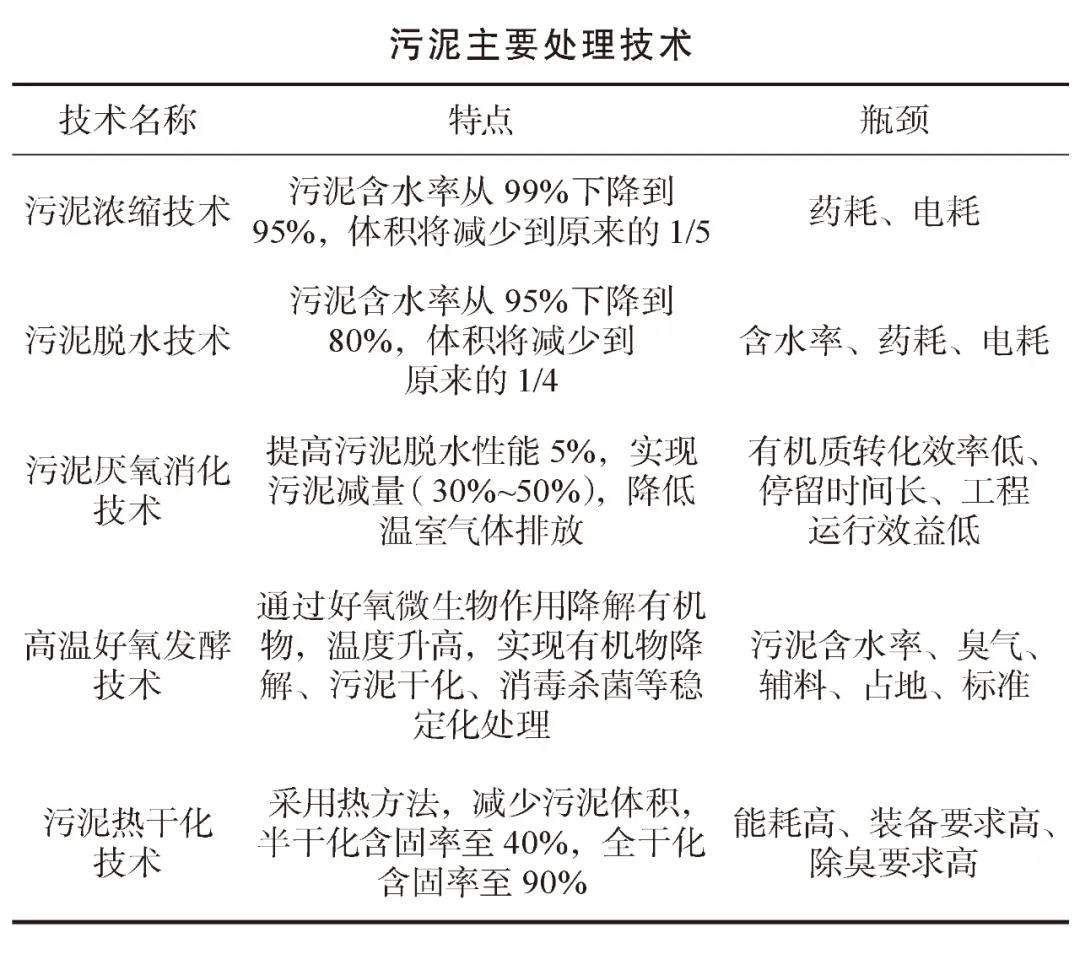
At present, the commonly used sludge treatment technologies in China mainly include sludge thickening technology, sludge dewatering technology, sludge anaerobic digestion technology, high temperature aerobic fermentation technology, and sludge thermal drying technology.
The treated sludge needs to be safely disposed of. At present, the disposal methods commonly used in China include land use (agricultural use), incineration, and sanitary landfill. However, these disposal methods have now encountered various degrees of obstacles: land use requires high sludge quality, and heavy metals and other toxic and harmful substances in sludge often exceed the standard. Due to the high water content of the sludge, the energy consumption of incineration is too high, which is not ecological and environmentally friendly; sanitary landfills usually encounter the embarrassing situation of no land to bury.
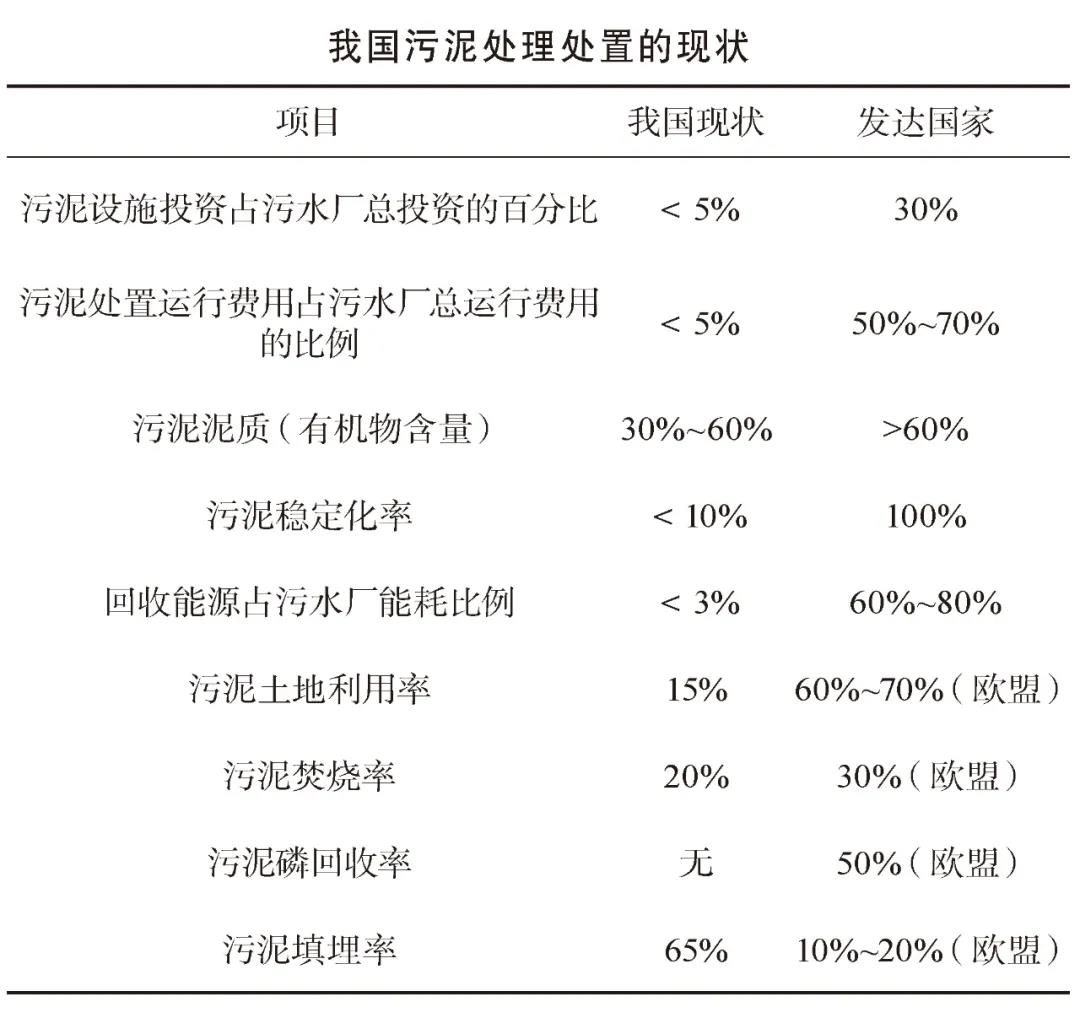
Due to the unclear subject of sludge treatment and disposal and the final disposal route, the imperfect regulatory system of laws and regulations, and the serious "heavy water and light sludge" phenomenon in the early construction of urban sewage treatment plants in China, the current sludge treatment facilities in China only basically achieve sludge The reduction of mud has not truly achieved the "three modernizations", and there is a serious risk of secondary pollution. According to statistics, the penetration rate of sludge anaerobic digestion is only 3%, which is far lower than the 50% level in developed countries. At present, the gap between China’s sludge treatment and disposal and developed countries is mainly reflected in: insufficient treatment capacity of sludge treatment facilities in China; insufficient sludge stabilization and resource utilization; insufficient green and ecological disposal methods.
Main technical route of sludge treatment and disposal
In response to large production of sludge and the severe treatment and disposal situation in China, the “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan” national urban sewage treatment and recycling facilities construction plan also clearly pointed out that sludge should be stabilized, harmless and recycled. During the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period, the investment of a large amount of scientific research funds enabled the rapid development of China’s sludge treatment and disposal technology. While introducing mature foreign technologies, closely focusing on the low organic matter content and high sand content of China’s sludge, four mainstream technology routes for stabilization and safe disposal have been formed: anaerobic digestion-land use, dry incineration-ash landfill or building materials utilization, aerobic fermentation-land use, and deep dehydration-emergency landfill.
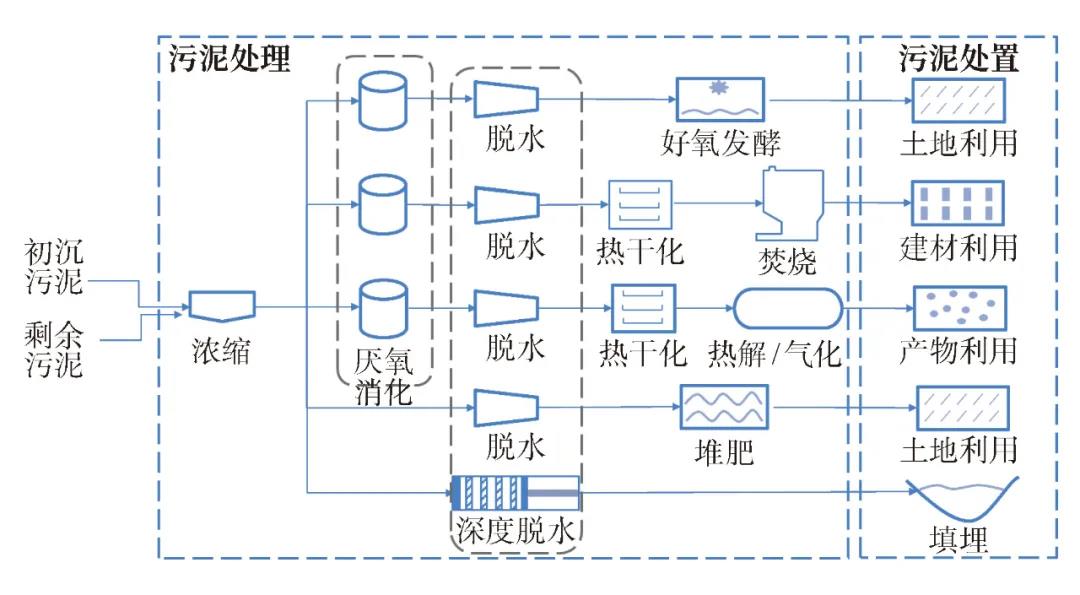
Anaerobic digestion-land use
Anaerobic digestion of sludge refers to the process in which biodegradable organic matter in sludge is decomposed under the action of facultative bacteria and anaerobic bacteria. With the stabilization of sludge, a large amount of biogas with high calorific value is generated as energy utilization and sludge resource utilization is realized. At the same time, the anaerobic digestion process is also a sludge reduction process, which can degrade 35%-50% of the volatile solids in the sludge, improve the dewatering performance of the sludge, and reduce the sludge by 30%-60% after dewatering. In recent years, anaerobic digestion has become the mainstream technology to realize resource recovery of sludge due to its economical, effective and sustainable advantages. Traditional anaerobic digestion usually refers to the use of medium temperature (35~37℃) or high temperature (52~55℃) for anaerobic digestion of concentrated sludge (with a solid content of about 5%),which has disadvantages such as low gas production rate per unit volume, low organic load, and unobvious engineering benefits Therefore, our country has developed a series of advanced anaerobic digestion technologies such as high-solid anaerobic digestion, thermal hydrolysis pretreatment, and coordinated anaerobic digestion during the 12th Five-Year Plan period, and they have been applied in actual projects. The advanced sludge digestion project of Beijing Gaobeidian Sewage Treatment Plant, the advanced anaerobic digestion demonstration project of Changsha Heimifeng sludge, etc. all adopt the "thermal sludge hydrolysis-anaerobic digestion" technology to improve the anaerobic digestion performance of sludge,reduce the H2S concentration in the biogas and improve the quality of the biogas. During the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period, explorations were also carried out on the synergy between sludge and kitchens and other organic matter, and demonstration projects such as the advanced anaerobic digestion of Zhenjiang sludge and kitchens were built. North row implements the technology of “high temperature pretreatment + anaerobic digestion” in five sludge treatment and disposal centers, “Gaobeidian”, “Xiaohongmen”, “Huaifang”, “Gaoantun” and “Qinghe No. 2” to realize the stabilization and harmlessness of sludge, and the products are used for soil improvement, nursery planting and fertilizer making, providing a model for the country's sludge resource utilization land use model.
Dry incineration—utilization of building materials
Sludge drying incineration technology refers to the process of first using thermal methods to evaporate sludge moisture into dried sludge, and then using aerobic combustion to mineralize the sludge. The ash residue after sludge incineration, first consider the use of building materials. The technology has high timeliness, can treat a large amount of sludge in a short time, and can recover the heat of incineration, and belongs to an internationally efficient technical means for sludge treatment and disposal. There are several projects in Shanghai, Zhejiang and other places in China. For example, the Shanghai Shidongkou sludge treatment project adopts fluidized bed sludge drying and fluidized bed incineration processes, which is the first domestic sludge drying and incineration project. In 2010, the Jiaxing Thermal Power Cooperative Sludge Disposal Project tried the first domestic sludge co-processing technology for co-combustion of sludge and coal. After the project is completed, the total annual power generation will be about 300 million kwh, saving about standard coal. 100,000 tons/year. In addition, the slag after incineration can also be used as a building material. This kind of collaborative incineration technology, which uses existing industrial incinerators to mix and incinerate dried sludge with other substances, is permitted under the laws of the European Union and Japan. Although from the perspective of investment and operating costs, coordinated incineration of sludge is more advantageous than separate incineration, but there is no relevant standard for coordinated incineration in China, and the problems of flue gas dilution, emission, monitoring and treatment of coordinated incineration need to be solved urgently. The development of dry incineration technology is still in its infancy. High energy consumption, high investment and operation requirements, and the treatment of odor and exhaust gas restrict the application of this technology.
Aerobic composting-land use refers to the process in which sludge is transformed into stable and harmless humification products (fertilizers) under certain moisture, C/N and ventilation conditions through the reproduction of aerobic microorganisms and degradation of organic matter in sludge to produce a higher temperature, so as to kill most parasites and pathogens in the sludge. After aerobic composting, the sludge produced by urban domestic sewage plants can reach the standards for restrictive agricultural use, landscaping and soil improvement, and the organic matter and nutrient elements in it can be effectively recycled. In addition, the construction, operation and maintenance cost of the sludge aerobic composting process is relatively low, the process operation and operation are relatively simple, and the process stability is high, which is more suitable for land use. Therefore, thermophilic aerobic fermentation has become a common sludge treatment technology in countries that encourage land use of sludge (such as Australia, etc.). During the 12th Five-Year Plan period, there have been a number of demonstration projects in China, such as the Qinhuangdao Lugang Sludge Treatment Plant, and developed intelligent control of high temperature aerobic fermentation technology and integrated drum aerobic fermentation equipment; however, due to the high water content of the sludge , Large area, limited outlets for malodorous gas products, etc., the promotion and application of this technology are restricted.
Deep dehydration-emergency landfill
The traditional landfill of sludge in China mostly adopts the direct landfill method of dehydrated cake (water content 75%~85%), which has caused a large number of environmental problems, mainly manifested as occupying a large amount of land resources, producing a large amount of leachate, causing groundwater and Surface water pollution destroys the original ecological environment. The root cause of these problems is the lack of stabilization treatment and sufficient moisture reduction at the front end. Therefore, in recent years, deep dehydration-landfill technology has emerged. Deep dehydration is a unique dehydration process in China. This technology can break the cell wall through conditioning and pretreatment, release capillary attached water and intracellular water, and improve the dehydration performance of sludge, thereby reducing the moisture content of sludge to below 60% . At present, the more mature sludge deep dehydration technologies include acid treatment, advanced oxidation technology and heat treatment and other physical and chemical methods, as well as biodegradation methods such as bioleaching and enzyme treatment, so that the dewatering performance and economic efficiency of sludge can reach the optimal conditions. Subsequent use of mechanical pressure dehydration and new plate and frame filter press filter press dehydration technologies for dehydration. However, due to the serious problem of no land to bury, landfilling does not conform to the future development trend and can only be used as a phased and emergency transitional technology, and cannot become a mainstream technology.
Engineering case of anaerobic digestion of mixed sludge
Anaerobic digestion, as the mainstream technology for sludge treatment and disposal in the world, can realize the stabilization and reduction of sludge, and also realize the recovery of biomass energy (biogas). However, due to long-term “heavy water and light mud”, The penetration rate of sludge anaerobic digestion is only 3%, and anaerobic digestion has three major bottlenecks: low organic matter conversion rate, low facility treatment load, and low engineering operation efficiency. Therefore, around the country’s urgent need to solve the technical problems of biological stabilization and resource utilization of sludge, the development of hydrothermal activation pretreatment, high-solid anaerobic digestion, sludge and kitchen and other organic matter collaborative anaerobic digestion technology has been developed for cities in China to provide sustainable development solutions for China’s urban sludge treatment.
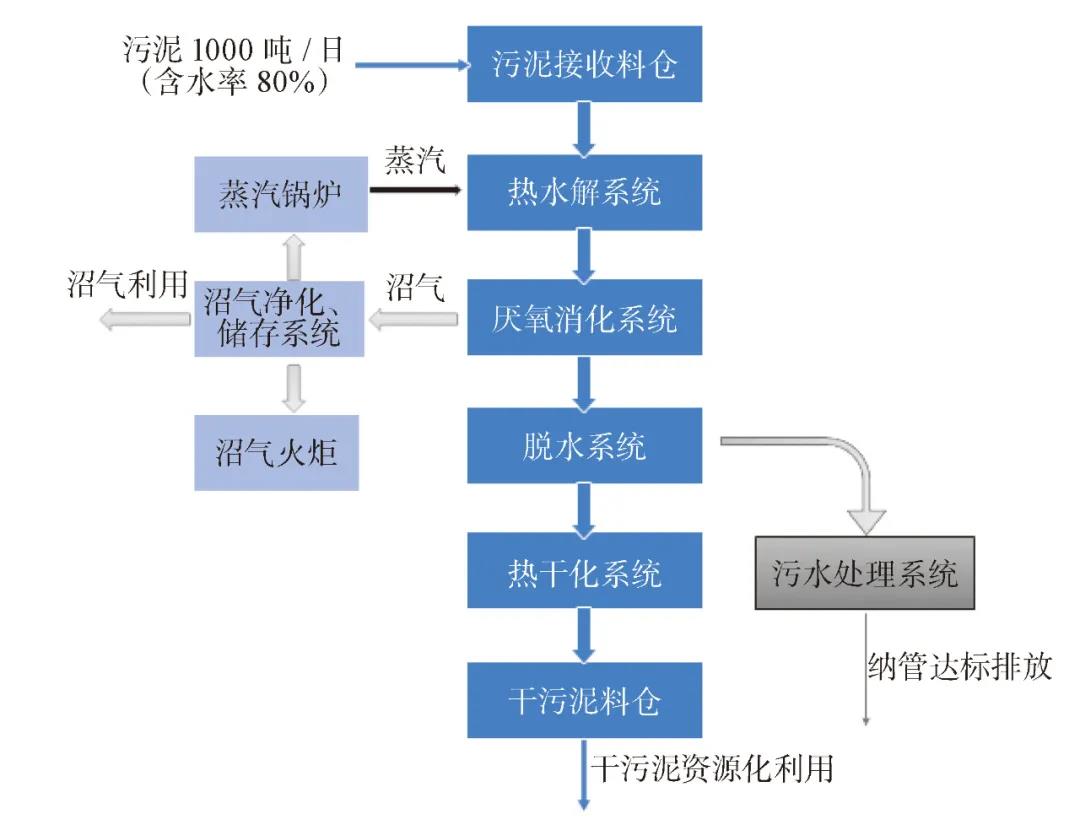
The sludge centralized disposal project of the sewage treatment plant in Changsha City
The sludge centralized treatment project of the sewage treatment plant in Changsha City adopts the advanced anaerobic digestion process of "thermal hydrolysis pretreatment of sludge + high-solid anaerobic digestion + sludge dewatering + drying", which is the first domestic demonstration project of sludge thermal hydrolysis coupled with high solids anaerobic digestion with independent intellectual property rights, and is also the first exploration of this technology in China, The daily processing scale is 500 tons/day (80% moisture content), and the total project investment is nearly 400 million yuan.
The incoming sludge of this project is conditioned by thermal hydrolysis pretreatment, the organic matter is dissolved, the viscosity is reduced, and the subsequent high-solid anaerobic digestion produces bio-energy biogas. The residue is dehydrated and dried and used as landfill cover soil. As a resource utilization and environmental treatment project, It effectively solves the problem of the outlet of urban domestic sludge.
Through the implementation of this demonstration project, a breakthrough has been made in the field of urban sludge biomass energy recovery-comprehensive resource utilization technology, which can solve the energy and resource problems of urban sludge treatment.
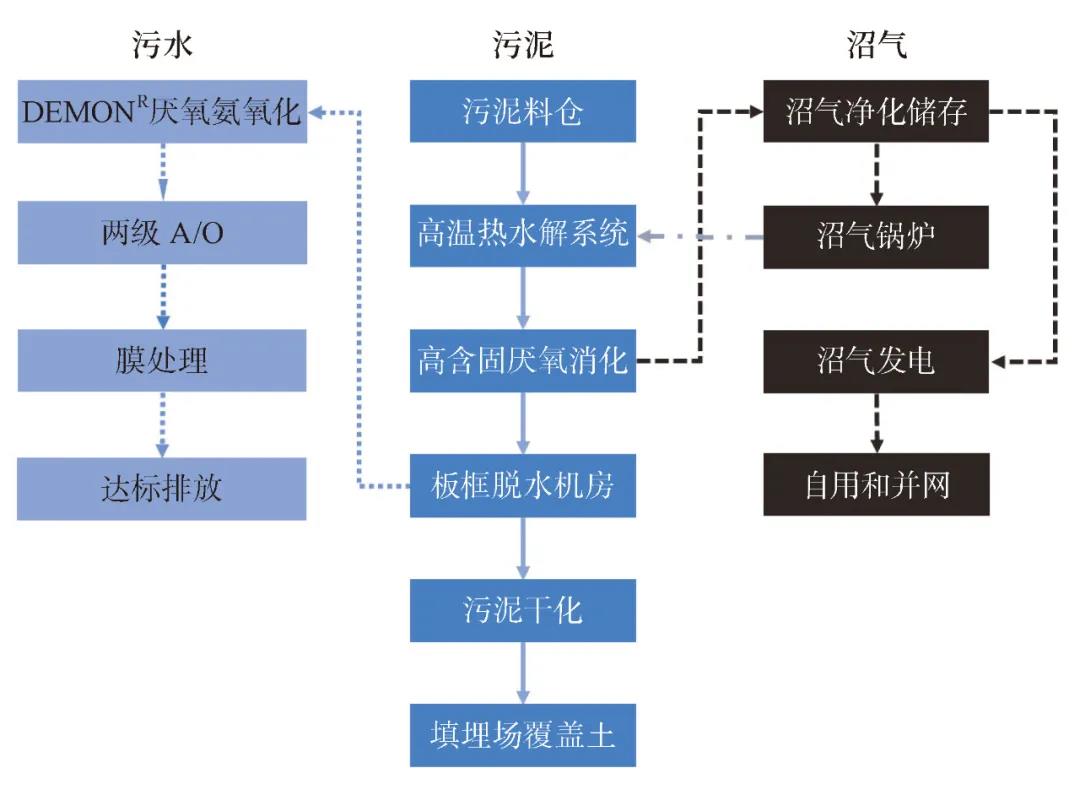
Demonstration project of advanced anaerobic digestion of sludge and kitchen in Zhenjiang
The Zhenjiang sludge and kitchen kitchen synergistic advanced anaerobic digestion demonstration project is the first domestic urban sewage plant sludge and kitchen waste coordinated anaerobic digestion project, which mainly adopts the process plan of "kitchen source pretreatment + sludge thermal hydrolysis + high solid content anaerobic digestion + biogas residue deep dehydration and solar drying utilization + biogas purification and purification to produce natural gas" with a daily processing scale of 260 tons/day, of which 140 tons/day of kitchen waste (including 20 tons of waste grease/day), 120 tons/day of sludge from urban sewage plants (80% moisture content), and a total project investment of nearly 180 million yuan, which can realize the "intelligent mixing" co-processing of sludge and wet garbage.
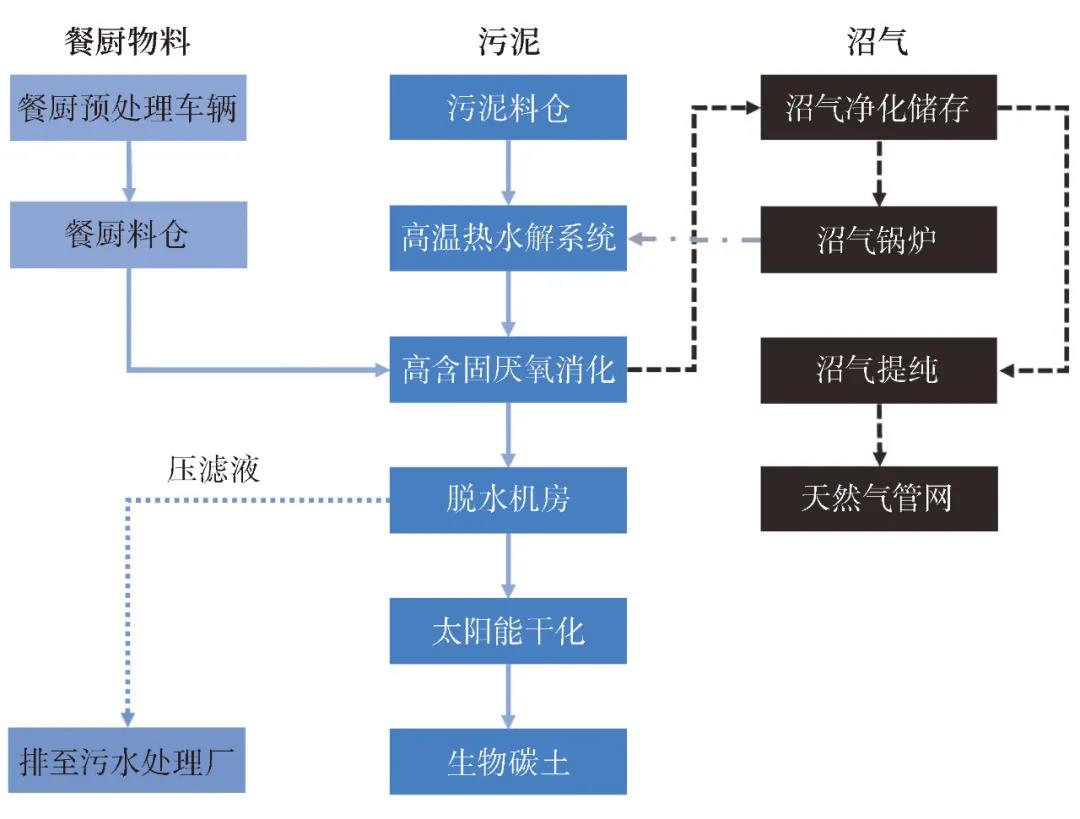
The project uses solar drying, which is beneficial to reduce the moisture content of the sludge after dehydration and fully realize the recycling of heat energy. The cooperative digestion of sludge and kitchen can also increase the volume utilization rate of digestion facilities and increase the organic load. At the same time, through the mutual dilution of the materials, the ammonia inhibition problem in the anaerobic digestion of high-solid sludge and the salt inhibition problem in the anaerobic digestion of food waste are obviously alleviated, and the process operation stability is improved. The project has more than doubled the methane production rate of the existing sludge anaerobic digestion facilities, and provided strong scientific and technological support for the implementation of national strategies such as "garbage classification" and "Yangtze River Protection".
Wastewater Treatment Plant Sludge Centralized Disposal Project in Xi'an
The advanced anaerobic digestion project of sludge constructed by Xi’an Sewage Treatment Plant Sludge Centralized Disposal Project is Xi’an’s first standardized and centralized sludge disposal PPP project, and it is also China’s first project with completely independent intellectual property rights. 1000 tons/day (80% moisture content), the monomer investment cost can be reduced by more than 40% compared with similar foreign technologies.
The project mainly adopts the process route of "thermal hydrolysis + anaerobic digestion + dehydration + thermal drying", and the processed end products can be used as landscaping and fertilizers to realize the harmless and safe treatment of sludge. The biogas produced after the treatment can be purified and desulfurized, and then used in boilers in the plant to provide heat for the entire plant.
Ways of recycling sludge
The sludge has a complex composition and is rich in resources such as organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus. The resource utilization of sludge focuses on two directions, namely, material recovery and energy utilization. Sludge can be used to recover energy through methods such as methane, hydrogen, and heat; it can also be recovered by extracting protein, polyhydroxy fatty acid (PHA), and phosphorus (P), as a carbon source for sewage denitrification and phosphorus removal, extracting recycling material, such as metalsand biocarbon soil, etc. The following describes some methods of sludge resource recovery-material recovery.
Protein recovery
The remaining sludge contains a large amount of organic matter, up to 70% of the dry weight of the sludge, and protein is the highest organic matter in the remaining sludge, accounting for about 40% to 60% of the organic matter. Relevant research shows that the remaining sludge organic matter contains 61 % Protein, 11% carbohydrates, less than 1% lipids and more than 27% unknown components. At the same time, protein is also the organic matter with the highest content in microbes, accounting for 50% to 60% of the dry weight of bacteria. The sludge is rich in protein and has great potential for recycling.
At present, methods for extracting and recovering protein from surplus sludge include physical, chemical, biological, and a combination of the above methods.
Protein extracted from sludge can be used as animal feed, crop fertilizer, etc. There are many related studies. Some studies have used the protein recovered from the surplus sludge as animal feed. After alkali treatment, ultrasonic treatment, acid precipitation and drying of the sludge, the protein nutrition content is equivalent to commercial protein feed, which proves that it is feasible to use crude protein recovered from surplus sludge as animal feed. Some studies have developed the production process of amino acid chelated microelement fertilizer using dehydrated sludge protein as raw material. Studies have been conducted on the recovery of protein from the wastewater of the second settling tank of a paper mill as a wood binder. There are studies using the excess sludge hydrolysate as a corrosion inhibitor, and its surface adsorption can effectively inhibit the corrosion reaction of steel in acidic media.
PHA
Traditional plastics are difficult to degrade and easily cause environmental problems. 4.9 million to 12.7 million tons of plastics have entered the ocean, which is expected to increase by an order of magnitude by 2025. In recent years, research on biodegradable plastics has attracted widespread attention. Biodegradable plastics are a type of plastic that can be degraded by microorganisms in nature or under certain conditions. Compared with traditional plastics, biodegradable plastics are easy to degrade and are not easy to cause environmental problems. Biodegradable plastics can be divided into different sources of raw materials: polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), PHA, etc. At present, PLA and PHA have been used in industrial production, but the higher cost of production raw materials makes their prices still higher than traditional plastics. Volatile fatty acids (VFA) are widely used in the production of PHA [14]. As an intermediate product of the anaerobic digestion process, especially the VFA produced in the acid-producing phase can be used as the raw material for PHA production. VFA produced by anaerobic digestion of sludge as the raw material can be used as the raw material of PHA, which can realize the resource utilization of sludge and reduce the production cost of PHA.
The anaerobic fermentation of sludge to produce VFA has been extensively studied. Under the conditions of pH 11, temperature of 60°C and fermentation time of 7 days, using sludge anaerobic fermentation, the maximum PHA yield is 56.5%. Studies have shown that VFAs produced by sludge fermentation are suitable carbon sources for the production of PHA.
Recovery of P
As a non-renewable resource, phosphorus is an essential element for living organisms. However, the excessive phosphorus concentration in natural water bodies and the lack of phosphorus resources are a basic contradiction. The transformation from the concept of phosphorus removal to phosphorus recovery is an inevitable trend. The sewage sludge is enriched with 95% of the total phosphorus (TP) in the raw water, and the recovery of phosphorus from the sludge has been extensively studied.
To recover phosphorus from sludge, the sludge needs to be pretreated first to fully release the phosphorus in the sludge. At present, pretreatment methods can be divided into biological methods and chemical methods. Biological methods such as anaerobic digestion and aerobic digestion, among which aerobic digestion is often combined with other methods. The chemical methods for releasing phosphorus from sludge include hydrothermal treatment, acid heat treatment, alkali heat treatment, oxidation pretreatment, and ultrasonic pretreatment. Methods for recovering phosphorus in sludge include adsorption and desorption, chemical precipitation, and struvite crystallization. Among them, the struvite crystallization method has been widely studied and applied because of its simple operation and simultaneous partial recovery of nitrogen.
Research Outlook
In recent years, around the basic principles of "reduction, stabilization, harmlessness, and resource utilization", China’s sludge treatment and disposal technology has made certain progress. Oxygen digestion technology and other sludge stabilization technologies have been well applied and promoted, and China’s policies and standards for sludge treatment and disposal are gradually improving. However, in the face of social development’s higher requirements for biomass energy and environmental quality, China’s sludge treatment and disposal needs to be harmless as the goal and resourceful as a means to vigorously develop technology of efficient recovery and utilizing energy and resources in sludge (clean biomass energy, nitrogen and phosphorus, etc.). While realizing the efficient recovery of energy resources in the sludge, it also realizes the stabilization or high-efficiency removal of pollutants in the sludge, improves the safety of subsequent use of sludge treatment products, and solves the problem of the ultimate outlet of sludge.
Facing climate change, shortage of energy resources, lack of environmental capacity and other issues, "resource recycling" is the focus of future new technology innovation, huge market demand and scientific and technological investment. It is believed that a batch of "new technologies for the utilization of sewage sludge" suitable for China’s national conditions will enter the market.
