Industry Insight | Comparison of five sewage fluoride removal technologies
Fluoride pollution has not been a new problem, but the importance of the last few years has increased significantly, the main photovoltaic, lithium batteries and other new energy industries can not be separated from the rapid development of the industry. In fact, in addition to the new energy industry, electronics and semiconductor industry, some metal processing and smelting, fluorine chemical industry, fluorite mining and other industries, will release fluoride, the wastewater of these industries have fluoride removal needs. In addition, the underground fluoride exceeds the standard in some areas, so drinking water plants that use groundwater sources also have the need for fluoride removal. Combined with different water quality and treatment scale and treatment needs, the fluoride removal technology usually used is not quite the same.
Currently, the technologies available in the market for fluoride removal are lime defluoridation (chemical precipitation method), aluminium salt defluoridation (coagulation precipitation method), ion exchange, adsorption method, and membrane method (RO technology).
01|Lime defluoridation
Lime defluoridation, commonly known as chemical precipitation method, generates CaF₂ precipitation by adding lime (CaO or Ca(OH)₂).
Ca(OH)2+2HF→CaF2↓+2H2O
Advantages are low cost and simple operation, but poor efficiency, especially when fluoride concentration is low. Lime defluoridation cannot remove fluoride to below 10mg/L, usually only to 10~15mg/L is already a better situation. This is mainly related to the solubility of CaF₂ itself, see below.
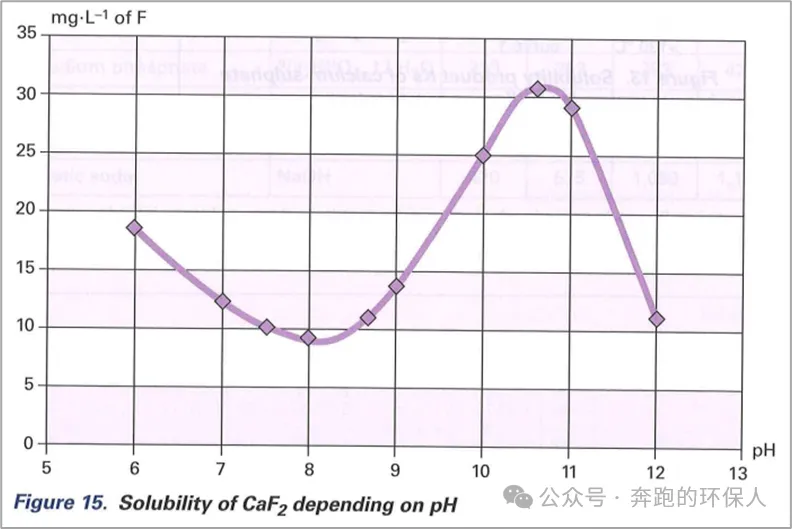
(from Deliman Water Treatment Manual)
The conclusion of lime defluoridation is as follows:
Advantages:
Low cost: lime is inexpensive and has low operating costs.
Simple operation: mature process, low equipment requirements, suitable for large-scale treatment.
Applicable to high concentration of fluorine: better effect on high fluorine sewage (e.g. industrial wastewater).
Disadvantages:
Fluorine residual concentration usually can only be reduced to 10-15 mg/L, which is difficult to meet the strict emission standards (e.g.<1.5 mg/L).
Large amount of sludge: a large amount of fluorine-containing sludge needs to be treated, and the stability of sludge is poor, which may cause secondary pollution.
High pH requirement: need to maintain pH>10, and then need to neutralise the sludge, which increases the cost.
02|Aluminium salt defluoridation
Aluminium salt defluoridation, commonly known as coagulation and precipitation method of defluoridation, is the removal of fluoride ions from water by adding aluminium sulphate, polymerized aluminium chloride (PAC), etc., using the complexation of aluminium salt with fluoride ions and the ligand exchange, physical adsorption, and sweeping action of fluoride ions by the intermediate products of the hydrolysis of the metal salts and colloidal alumina generated at the end.
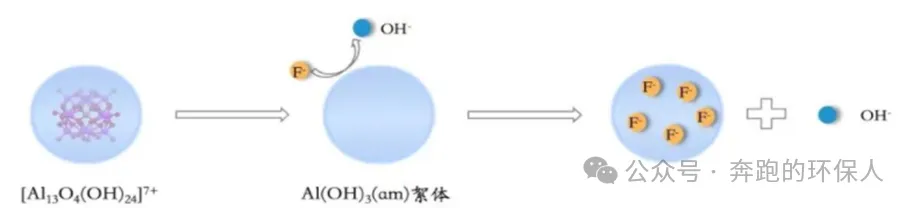
Of course, there are many manufacturers in the industry who produce special fluoride removal agents, and in the coagulation and precipitation method of fluoride removal, instead of aluminium salt fluoride removal, also has better results. Each manufacturer has its own formula for specialised fluoride removal agents, and the composition varies greatly. Therefore, the dosage and removal effect, there are also large differences.
Defluoridants are generally formed by combining metal compounds such as aluminium salts, iron salts and other metal compounds with fluoride ion adsorption materials to form a mixture. Analysing the defluoridating agents of various manufacturers, it can be found that there are three main types of substances in the components inside the defluoridating agent: aluminium/iron salts, adsorbents, and coagulation aids.
Coagulation and precipitation method of defluoridation concluded as follows
Adopting high-density sedimentation tank process, the addition of aluminium salt can achieve high defluoridation efficiency, which can reduce the fluorine concentration to less than 1.0 mg/L. It is suitable for water treatment plants with low and medium concentration of wastewater or groundwater as the source of water.
Higher requirements for the precipitation process, high automation requirements
High requirements for pH control, need to be precisely controlled in acidic conditions.
Conventional high-efficiency sedimentation tanks have a large dosage of chemicals, and the use of a special high-efficiency sedimentation tank for fluoride removal can significantly reduce the dosage of chemicals.
Risk of aluminium residue: Excessive aluminium may introduce secondary pollution (e.g. excessive aluminium ions)
03|Ion exchange method
Adsorption of fluoride ions (F-) by anion exchange resin, and restoration of adsorption capacity through regeneration. The advantage is that the treatment effect is good and it is suitable for low concentration, but the regeneration requires acid and alkali, the cost is high, and the resin is easily contaminated by organic matter, and there is some treatment efficiency and resin life when the SS in the water is high. Generally, it is suitable for the occasions with low concentration and high requirements for the effluent, such as drinking water treatment.
Good treatment effect: the fluorine concentration of the effluent can be lower than 1 mg/L, which is suitable for low concentration treatment, and it is more suitable for small-scale drinking water treatment because of the high requirement of SS of the influent (high requirement of pre-treatment).

Ion exchange method for fluoride removal
Higher operation cost, resin regeneration needs acid and alkali or salt solution, which produces high salt wastewater
High fluorine concentration of regeneration solution also needs extra treatment, usually also treated by coagulation and precipitation
Resin is easy to be clogged by organic matter suspended matter causing pollution, and the requirement for pretreatment is strict
System operation and maintenance is more complicated, and the operation requirement is high
Overall, the ion exchange method is suitable for low-concentration fluorine-containing wastewater and has high requirement for pretreatment. Since the cost is also high, it is more suitable for the treatment of drinking water with small and medium volume.
04|Adsorption method
Selective adsorption of fluoride ions by adsorbents such as activated alumina, bone carbon, zeolite, nanomaterials, etc. There are many kinds of adsorbents. There are many types of adsorbents with different adsorption capacities and removal effects, and some adsorbents can be regenerated and reused, while others cannot be regenerated. However, due to the limitation of adsorption capacity, it needs to be replaced or regenerated frequently, and the operation cost varies greatly with different materials. In the field of fluoride removal, activated alumina adsorbents are more widely used.
![]()

(Picture from the Internet)
Characteristics of fluoride removal by adsorption
Applicable to low concentration: good effect on low fluoride wastewater (e.g. rural decentralised drinking water).
Renewability: some adsorbents (e.g. activated alumina) can be reused through regeneration.
Limited adsorption capacity: frequent replacement or regeneration is required, and the operation cost fluctuates with different materials.
Pretreatment needs: when the water quality is poor, such as high turbidity and high organic matter, pre-treatment is required.
Material cost varies greatly: e.g. nanomaterials are efficient but expensive, bone carbon is cheap but easily saturated.
05|Reverse osmosis defluoridation
Fluoride ions and other dissolved pollutants are trapped by driving wastewater through a semi-permeable membrane by a high-pressure pump. Since the reverse osmosis membrane (RO membrane) is a semi-permeable membrane, it is able to remove fluoride ions from water by blocking most ions and molecules and allowing only water molecules to pass through it.RO removes ions with a broad spectrum, and therefore removes a wide range of ions, including common chlorine ions, sulphate ions, sodium ions, calcium ions, etc., in addition to fluoride ions. Therefore the quality of the effluent water is very good, but the cost is very high.
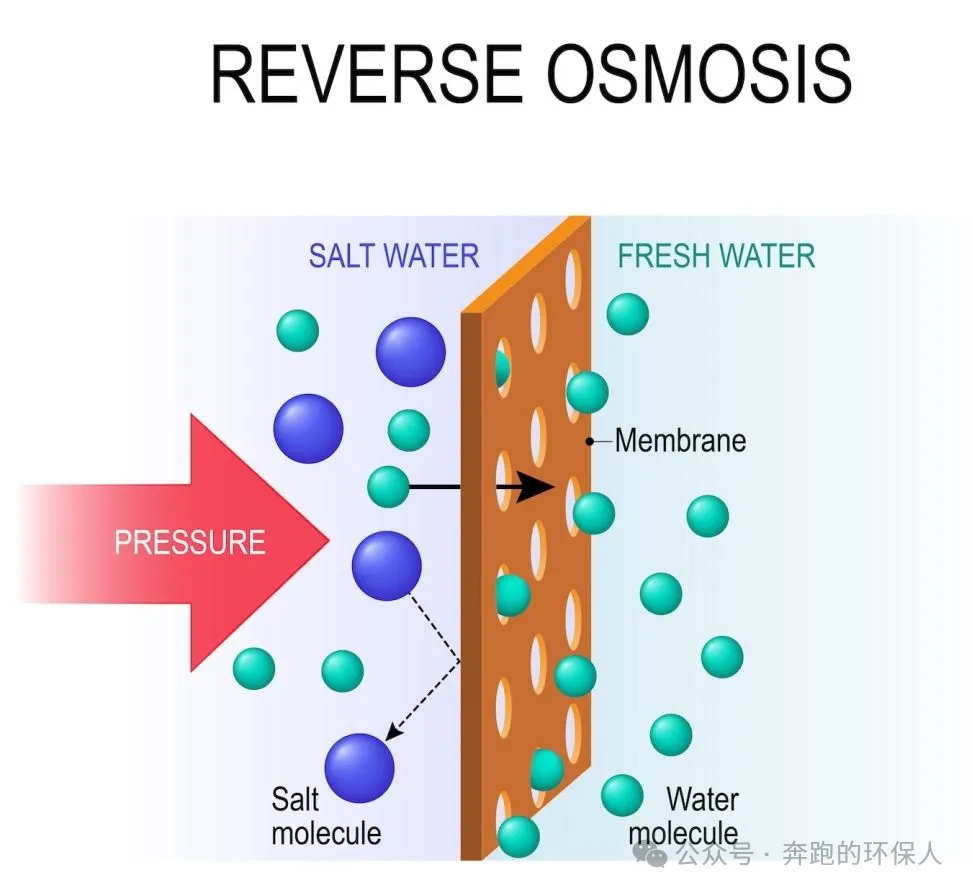
(Picture from the Internet)
Features of fluoride removal by reverse osmosis
Good quality of effluent water, up to 0.1-0.5mg/L, meets the most stringent standards (e.g., drinking water)
No sludge production
Large investment cost, high energy consumption, high maintenance cost
Strict pretreatment is required to prevent membrane contamination, otherwise it is very easy to block
The concentrated water produced is difficult to treat, with a high fluorine content, and requires further treatment
06|Comprehensive Comparison
Comprehensive In terms of investment, operation and treatment effect, the recommended industries for fluoride removal in industrial parks and industrial wastewater under different circumstances are as follows:
High-fluorine wastewater, suitable for lime method
Medium-low concentration (10-15mg/L) fluorine wastewater, coagulation and precipitation method is recommended for fluoride removal, which can be processed up to 1.5mg/L or even below 1.0mg/L
Decentralised/small-scaled low-fluorine wastewater, can be adsorbed only
Low fluorine with exceptionally strict emission standards (less than 1 or even less than 1.0mg/L) Low fluorine and emission standard is very strict (less than 1 or even 0.5mg/L), reverse osmosis membrane treatment or ion exchange method can be considered.
Of course, even if the coagulation and precipitation method of fluoride, there is a considerable technical content, to do a good job, but also need real skills. Because as I often say, there are a lot of efficient precipitation tanks are actually not efficient ....
Comprehensive point of view, in the large-scale sewage defluoridation, high density pool defluoridation application of the most, of course, the application of special defluoridation high density pool, compared with the ordinary high-efficiency sedimentation tank, saving 40 ~ 50% of the amount of chemicals added at the same time, to ensure that the concentration of water can be less than 1.5 or even 1.0.
